How Long Until a Tooth Infection Kills You?
In rare but serious cases, a tooth infection can become fatal in just days if it spreads to the brain, heart, or bloodstream. The timeline depends on how fast the infection spreads and the person’s immune system. While most cases progress over weeks, untreated infections have led to death in under a week. Immediate treatment with antibiotics and dental care is critical to prevent life-threatening complications like sepsis or brain abscess.
Understanding Tooth Infections: Causes and Symptoms
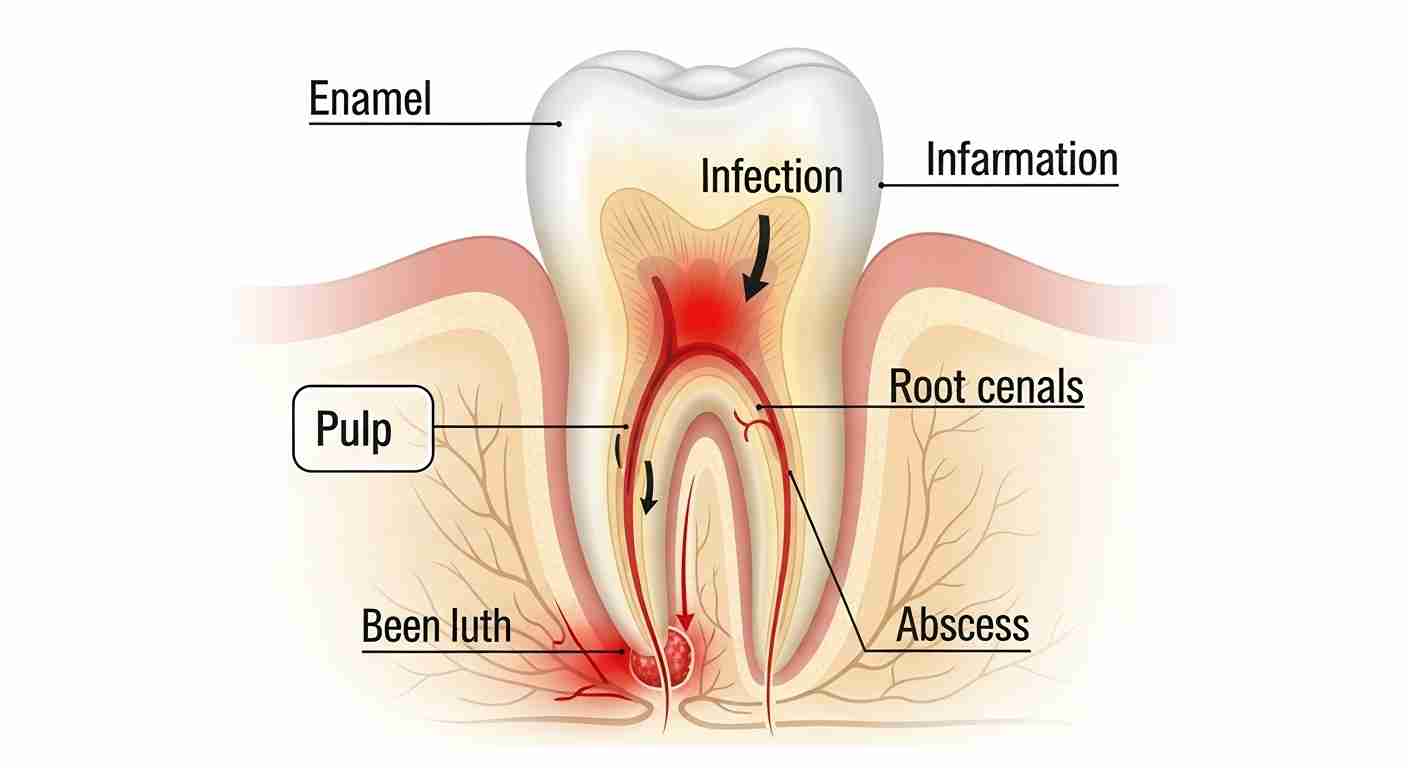
Tooth infections, also known as Dental abscess¹, occur when bacteria invade the tooth's inner layers due to untreated decay, fractures or damage. These infections typically spread to the pulp, containing nerves and blood vessels, leading to inflammation and pus buildup. Poor oral hygiene, a high sugar diet or trauma to the teeth significantly increase the risk.
Symptoms vary but often include severe toothache, sensitivity to hot or cold, swelling in the gums or face and a foul taste in the mouth from pus leakage. In advanced cases, fever, difficulty chewing or swollen lymph nodes may occur, signaling systemic spread. Prompt treatment is crucial.
How Bacteria Spread: The Science Behind Tooth Infections
Tooth Infections typically originate from bacterial invasion into the inner layers of a tooth. Such infections often starts in the pulp, a soft tissue containing blood vessels and nerves. Bacteria gain access through cavities, or cracks, or trauma. Multiplying rapidly as they feed on decayed material. As the infection grows, pus filled pockets, known as abscesses, may form, leading to localized pain and swelling.
The infection may spread via the bloodstream if left untreated and potentially causing systemic complications. common pathways include lymphatic vessels² or direct infiltration into surrounding tissues. Transitioning from mild discomfort to severe outcomes depends on multiple factors such as immune response types of bacteria and prompt treatments.
Stages of a Tooth Infection: From Mild to Severe
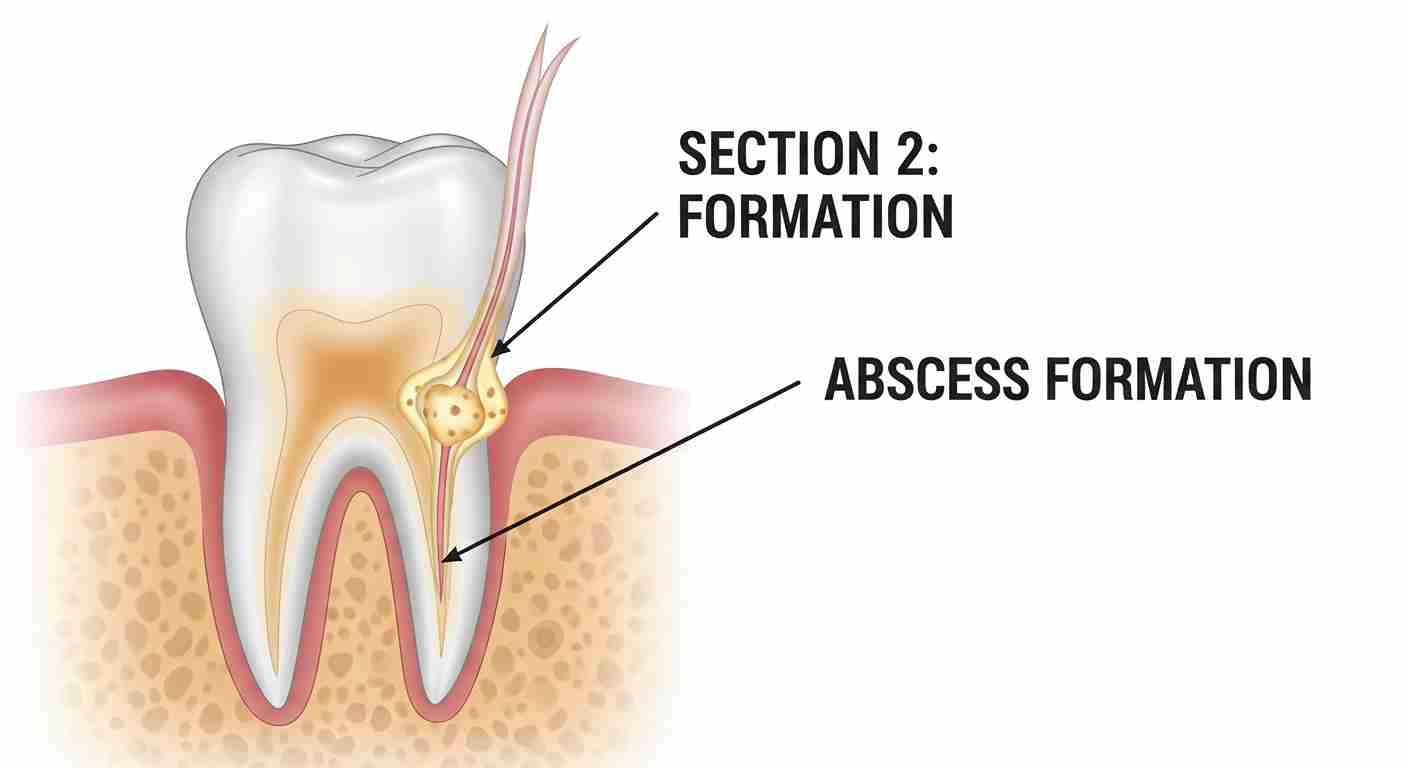
Tooth infection progress through several identifiable stages, each reflecting the severity of the condition:
- Initial Stage - Pulpitis: The infection begins in the pulp, Often producing mild discomfort with swelling and sensitivity to temperature changes. At this stage, bacterias attack the dental pulp³ inside the teeth.
- Second Stage - Abscess Formation; Left untreated, the infection spreads to surrounding tissues, Leading to a localized pus-filled abscess. This stage may cause intense pain, and gum inflammation and visible swelling near the infected tooth.
- Advanced Stage - Spreading infection: The bacteria infiltrate adjacent areas, including jawbone and facial tissues. Symptoms can include fever, fatigue and difficulty chewing or speaking.
Some advanced facial treatments may target skin inflammation, which, if combined with poor oral hygiene, could contribute to recurring facial infections.
- Critical Stage -Systemic Spread: As the infection enters the bloodstream (sepsis⁴), it can affect vital organs, potentially resulting in Life-Threatening complications such as heart infections or respiratory distress.
Early Warning Signs That Shouldn't Be Ignored
Recognizing the initial symptoms of a tooth infection is key to preventing serious complications . Early signs often include localized pain or sensitivity, particularly when biting or chewing. Patients May notice redness or swelling around the infected tooth or gums. Persistent bad breath and an unpleasant taste in the mouth can indicate bacterial activity.
Other signs include the development of a pimple-like swelling on the gum, which may discharge pus. Systemic symptom such as fever, fatigue, or swollen lymph nodes near the jaw or neck should raise concern. If the pain radiates to the jaw, ear or face, Immediate medical attention is crucial.
Complications When Tooth Infections Go Untreated
When tooth infections are left untreated, These can result in serious health complications due to the spread of bacteria. The infection may advance beyond the tooth and gums, entering the bloodstream, A condition known as sepsis. Sepsis can lead to organ failure, dangerously low blood pressure, and even death. Additionally, Untreated infections can cause abscesses, which may damage surrounding tissues and bone. In extreme cases, bacteria from the infection may travel to the brain or lungs, causing meningitis or a lung abscess. if intervention is delayed, then permanent damage to oral health and overall well being may occur, Underscoring the importance of timely treatment.
When a Tooth Infection can Become Life-Threatening
If a tooth infection is left untreated, then it has the potential to escalate into severe health related complications. The dental infection can spread beyond the teeth and gums, leading to conditions like cellulitis, sepsis or endocarditis⁵. in rare cases, tooth infection may cause Ludwig’s Angina⁶, An aggressive infection of the neck and lower jaw, obstructing the airway.
Risk factors include:
- A weakened immune system
- Lack of timely dental care
- Uncontrolled Diabetes
Symptoms such as difficulty breathing or high fever or severe facial swelling may indicate a medical emergency. Prompt intervention is crucial to prevent systemic spread and life threatening outcomes.
Conditions That Increase Risk For Severe Outcomes
Certain medical conditions or circumstances can heighten the risk of severe complications when dealing with a tooth infection:
- Compromised Immune System; Individuals with weakened immune systems, Such as those undergoing chemotherapy, organ transplant recipients, Or individuals with HIV/AIDS, are more vulnerable to severe infections
- Chronic Conditions: people with diabetes, heart disease, or respiratory disorders may experience heightened risk as infections can escalate quickly in these populations.
- Age factors: Elderly individuals, Whose immune response may be diminished and young children, whose immune systems are underdeveloped, All are particularly at risk.
- Delayed Treatments: Prolonged delays in seeking dental or medical care can exacerbate the infection, increasing the potential for life threatening complications like sepsis.
Preventative Measures: Avoiding Tooth Infections
Preventing tooth infections begins with maintaining proper oral hygiene. Individuals should brush their teeth at least twice daily using fluoride toothpaste and an ADA Approved toothbrush. Flossing regularly helps remove plaque and debris from between the teeth and gum line, areas a toothbrush cannot reach. Scheduling dental checkups every six months ensures early detection of cavities, decay or gum diseases. Consuming a balanced diet rich in nutrients, While limiting sugary and acidic foods, Aids in strengthening teeth and preventing bacterial overgrowth. Avoiding tobacco products, which increase the risk of dental infections or oral infections, is strongly advised. Prompt attention to dental discomfort is critical to preventing serious complications.
Maintaining overall body hygiene, including the use of skin-safe products like natural deodorants, may also contribute to reducing harmful bacterial activity.
Treatment Options for Tooth Infections: What’s Effective?
Effective oral/dental treatment for tooth infections or teeth pain often begins with professional dental care. Dentists typically prescribe antibiotics to combat bacterial infections and reduce swelling. Common antibiotics include amoxicillin, penicillin, or clindamycin. For severe infections, a dental treatment procedure may be necessary.
Common Treatment Options:
- Drainage: The Dentist may puncture the abscess and drain pus to relieve pressure.
- Root Canal: infection removal from the root is performed to save the tooth.
- Extraction:If the tooth cannot be salvaged, then removal is recommended.
- Pain management: Analgesics help alleviate discomfort during treatment.
Ignoring proper dental care can worsen infections and risking severe complications. Therefore prompt intervention is vital.
Timelines for Seeking Medical Attention: When to Act
A tooth infection requires prompt medical attention to prevent dental complications. Immediate action is essential if symptoms such as severe pain, or swelling of the face or neck, fever, or difficulty swallowing are experienced. These signs may indicate the oral infection has spread beyond the tooth.
Seek care within 24 to 48 hours if mild discomfort or swelling persists, As early treatment can prevent escalation.
If breathing or vision is compromised due to swelling, dental emergency services must be contacted immediately. Waiting longer than a few days for dental treatment risks extended suffering and the development of serious health conditions.
FAQs:
1. Question: What causes a tooth infection, and what are the symptoms?
Answer: A tooth infection, also known as a dental abscess, is caused by bacteria invading the tooth pulp or surrounding tissues due to decay, cracks, or injury. Symptoms include pain, swelling, sensitivity to temperature or pressure, bad breath, and sometimes fever.
2. Question: How do bacteria spread in a tooth infection?
Answer: Bacteria spread in a tooth infection through the tooth's layers into surrounding tissues, potentially entering the bloodstream or spreading to other areas of the body if left untreated.
3. Question: What are the stages of a tooth infection from mild to severe?
Answer: A tooth infection progresses through different stages: mild symptoms like localized pain and sensitivity, severe infection with swelling, pus formation, and potential spread to other body areas, which can become life-threatening.
4. Question: What are the early warning signs of a tooth infection?
Answer: Early warning signs of a tooth infection include persistent toothache, tooth or gum swelling, redness, sensitivity to temperature, and foul-tasting fluids in the mouth.
5. Question: What complications can arise if a tooth infection goes untreated?
Answer: Untreated tooth infections can lead to serious complications such as the spread of infection to the jaw, face, or other areas, sepsis, difficulty breathing, and in rare cases, death.
6. Question: When can a tooth infection become life-threatening?
Answer: A tooth infection can become life-threatening when bacteria spread to vital areas, such as the bloodstream (causing sepsis), brain (causing abscesses), or airways (causing difficulty breathing). Immediate medical attention is needed.
7. Question: What conditions increase the risk of severe outcomes from a tooth infection?
Answer: Conditions such as weakened immunity, diabetes, heart disease, and delayed medical treatment can increase the risk of severe outcomes from a tooth infection.
8. Question: How can tooth infections be prevented?
Answer: Tooth infections can be prevented by maintaining good oral hygiene, regular dental check-ups, treating cavities and injuries promptly, and avoiding sugary foods that promote decay.
9. Question: What are the effective treatment options for tooth infections?
Answer: Treatment for tooth infections typically includes drainage of the abscess, antibiotics to fight the infection, and dental procedures such as root canal or extraction to address the underlying issue.
10. Question: When should you seek medical attention for a tooth infection?
Answer: You should seek medical attention as soon as symptoms like severe pain, swelling, fever, or difficulty breathing appear. Delaying treatment can lead to serious complications.
11. Question: What is Brain Abscess?
Answer: Brain abscess is a serious condition where pus collects in the brain due to an infection, causing swelling, fever, and neurological symptoms like headaches or confusion.
Definitions of Medical Terms:
¹ Dental Abscess: A Buildup of pus caused by a bacterial infection inside the tooth or gums, Typically resulting from untreated tooth decay or trauma.
² Lymphatic Vessels; Thin walled structures that help carry lymph (A fluid containing infection-fighting white blood cells) throughout the body. Infection can spread through this system.
³ Dental Pulp: The soft and innermost part of a tooth that contains nerves and blood vessels. infection of this area can lead to intense tooth pain and inflammation.
⁴ Sepsis: a life threatening response to infection where the body’ s immune system causes damage to its own tissues and organs. It can result from the spread of a tooth infection into the bloodstream.
⁵ Endocarditis: An infection of the inner lining of the heart chambers and valves, Often caused by bacteria entering the bloodstream, including from untreated dental infections
⁶ Ludwig’s Angina:A serious bacterial infection of the floor of the mouth and neck that can obstruct airways and become life-threatening if not treated immediately.















Vestibulum euismod, leo eget varius gravida, eros enim interdum urna, non rutrum enim ante quis metus. Duis porta ornare nulla ut bibendum
Rosie
6 minutes ago